Lubrication is an important aspect of any auto vehicle; therefore, select oil when maintaining your engine. From the process of lubricating, the engine oil also has a function of cooling, cleaning, and preventing the occurrence of wear in the engine. In the list of the provided choices, 10W-30 and 10W-40 are two of the most frequently used types of engine oil. But which one is best for your engine? Let me enlighten you with more information and see if this is true.
Understanding Engine Oil Grades

So, to understand the differences between 10W-30 and 10W-40, it is vital to know what these numbers refer to. SAE is the society that has established classes of engine oil grades. The figures indicate the grade based on the oil’s viscosity, accompanied by ‘W’ for Winter.
10W-30 Engine Oil
Characteristics
10W-30 is an example of an engine oil where W stands for winter. Thus, 10W means it has 10 viscosity at the freezing point and 30 at the running temperature of the engine. This implies that, at low temperatures, the oil is comparatively thin; hence, starting is easy, and rapid lubrication is achieved.
Benefits
- Fuel Efficiency: Lighter oils such as the 10W-30 raise fuel mileage since they lead to lower engine drag.
- Cold Weather Performance: This is because it has a thin consistency when cold, which enables the engine to start easily and is supplied with the correct amount of lubrication faster.
- Engine Protection: Affords the necessary protection and lubrication to most modern-day engines.
Best Use Scenarios
- This is suitable for car use in areas that experience mid-range to Cold climates.
- Applicable for those vehicles that make many relatively short trips within a short time.
10W-40 Engine Oil
Characteristics
10W-40 engine oil has a viscosity of 10, which indicates the oil’s thickness when it is cold, and 40 is the thickness of the engine oil at the engine’s running temperature. This results in it making it thicker at higher temperatures than 10W-30.
Benefits
- Better High-Temperature Protection: Thicker oil offers higher protection, and when a car is in a hot region, thick oil may be the best choice.
- Engine Durability: It gives better lubing for older cars with more mileage than new ones.
- Reduced Oil Consumption: Thicker oil will always limit the amount of oil an engine uses in its operations; the truth behind this is that.
Best Use Scenarios
It is most suitable for use in cars in alternately hot and cold areas or in hot climates.
It is ideal for older cars or those that have traveled a great distance while being used frequently.
Viscosity Explained
What is Viscosity?
Viscosity simply means how thick a type of oil is or how much that oil will resist flowing. Higher viscosity means the oil is thicker and does not flow as fast as the lower-viscosity oils, which are comparatively thinner.
Impacts of Viscosity on Engines
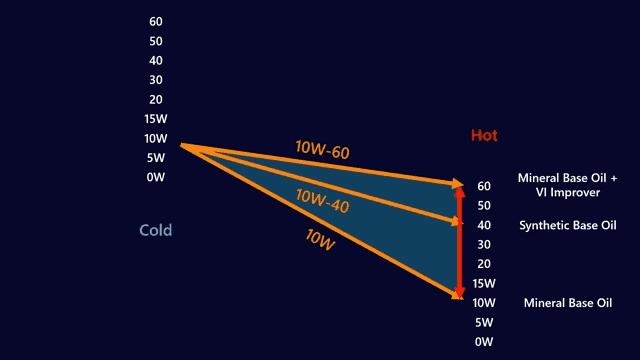
Thus, we see that the viscosity of the oil, which is the resistance of the oil to flow, influences the possible ability of the engine to be lubricated more or less, depending on its temperature. Low-viscosity ones enable good flow at low temperatures and guarantee timely lubrication of the engine parts when the engine is started in the morning. In general, the thicker oils, that is, the oils with higher viscosity, are more protective at higher temperatures.
Temperature Considerations
Cold Weather Performance
Conversely, the 10W-30 oil lighter kind means the oil starts to flow easily in cold climates and reaches the various parts of the engine when the vehicle is started.
Hot Weather Performance
In hot conditions, this thicker oil, such as 10W-40, is ideal because it retains a higher viscosity and is capable of forming a layer of oil over the surfaces of the engine to minimize friction and wear.
Fuel Economy

Selecting the right oil can also affect your car’s fuel economy to whatever extent it may be. Oils with numbers such as 10W-30 are thinner; consequently, their friction and drag in the engine can be lower, and, therefore, they end up being more effective in terms of fuel consumption. On the other hand, 10W-40 might provide better protection, but at the same time, this oil type is slightly thicker, which has an impact on fuel consumption.
Engine Wear and Tear
Thus, the proper choice of oil provides an effective way to fight against wear and tear in the engine. The thin oils offer improved lubrication during cold start; hence, the incidences of wear are low. On the other hand, thick fluids are able to retain the protection they provide to the engine at high temperatures, that is, during long journeys and especially when the climate is dry.
Manufacturer Recommendations
Check the manufacturer’s guide for the vehicle; it will show you the type of oil recommended for your car. Below are my suggestions and made them;
I make my recommendations with the given tests and your engine requirements in mind.
Importance of Following Manufacturer Guidelines
This way, the recommended oil helps your engine perform to the best of its capabilities and stay safeguarded. Deviation from this recommendation may not only cause massive wear but also shorten the lifetime of the engine.
How to Find the Recommended Oil for Your Vehicle
Check the owner’s manual or consult the manufacturer’s website. You can also find this information on the oil filler cap or dipstick.
Driving Conditions
Urban vs. Highway Driving
Road conditions affect the possibility of choosing the right oil for your vehicle’s engine. The stop-and-go driving experienced in urban areas is ideal for thinner oil types, which range from 10W-30 and are thin and thus fast to lubricate. Highway driving, characterized by longer distances and high speeds, might require extra protection from a thicker oil such as 10W-40.
Impact of Driving Habits
High-speed driving with jerks and sudden acceleration leads to more wear on the engine and hence requires oils up to 10W-40.
Oil Change Intervals
Recommended Intervals for 10W-30
Change intervals that are most commonly recommended for 10W-30 oil are between 3,000 and 5,000 miles, provided that they correspond with the recommendations of the vehicle manufacturer.
Recommended Intervals for 10W-40
There is not much difference, and the 10W-40 oil change interval is also almost the same, and it lies around 3000 to 5000 miles. Nevertheless, the specifics should be sought in the manual of the respective vehicle.
Synthetic vs. Conventional Oil
Synthetic oil and conventional oil are two types of oil that may be used in an auto engine, with each having the following characteristics:
Compared to the original kinds of oil, synthetic oils boast better qualities and capabilities for protecting and operating a car. They do not react with metals, are more stable at high temperatures than conventional lubricants, and give better protection at a cold start.
What is the difference between 10W-30 and 10W-40?
The two are 10W-30 and 10W-40 oils, which also exist in synthetic and conventional types. While these are slightly more costly, synthetic oils offer better protection and performance than conventional oils and are thus preferred for both types.
Conclusion
It all boils down to the car’s specification and the environment in which you frequently use it to determine whether you stick with 10W-30 or opt for the 10W-40 potency. Each oil is helpful and requires a different context to be applied. It is always advisable to consult the owner’s manual of your vehicle and think through the normal driving patterns and environment to make the best choice for your engine.
FAQs
Is it okay to switch between 10W-30 and 10W-40?
Yes, you can switch between these oils, but it’s essential to consider the manufacturer’s recommendations and the climate you’re driving in.
Can I use 10W-40 In a car that recommends 10W-30?
Using 10W-40 in a car that recommends 10W-30 might provide extra protection in hot climates, but it is best to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines.
How often should I change my oil?
Oil change intervals depend on the oil type and driving conditions. Typically, they range between 3,000 and 5,000 miles.
What happens if I use the wrong oil?
Using the wrong oil can lead to increased engine wear, reduced performance, and potentially voiding your warranty.
Are there any other oil grades I should consider?
Depending on your vehicle and climate conditions, grades like 5W-30 or 0W-40 might be recommended. Always check the owner’s manual.