Hybrid cars use a gasoline engine and an electric motor to improve fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, and improve performance by switching between or combining the two power sources as needed.
Such types of automobiles as hybrid cars, which are equipped with traditional combustion engines modified by the additions of electric systems, have gained great popularity among those people who care about climate. But where do such vehicles come from? This special article will focus on a detailed description of how hybrid cars operate, the advantages and disadvantages of using this technology, and where the further development of hybrid cars is headed.
Understanding the Basics of Hybrid Cars

What Makes a Car Hybrid?
Definition of Hybrid Cars
A hybrid automobile employs more than one type of energy on board to produce motion or movement. Usually, such a plant consists of a gasoline-fueled internal combustion engine and an electric motor driven by a battery set. The target is the optimization of fuel consumption and emission coefficients.
Different Types of Hybrid Cars
Hybrids are not equal in design; some differ from others in terms of interface and features. Today, there is a full hybrid, a mild hybrid, and a plug-in hybrid – and each of them has its parameters. In full hybrids, both the electric motor and the ICE, as well as both in parallel, can be operated, while in mild hybrids, the electric motor helps propel the ICE. PHEVs can be recharged from an external source and hence can be driven for longer distances using electricity alone.
Hybrid vs. Traditional Combustion Engines
Fuel Efficiency
Another benefit of hybrid cars over conventional combustion engine-powered cars is that they are much more fuel efficient. Hybrids cut down on the use of gasoline through the use of an electric motor, particularly in low-speed city driving.
Environmental Impact
Cars that are hybrid emit less than non-hybrid cars. The electric motor permits cleaner driving, especially in city traffic, where ordinary engines are less efficient.
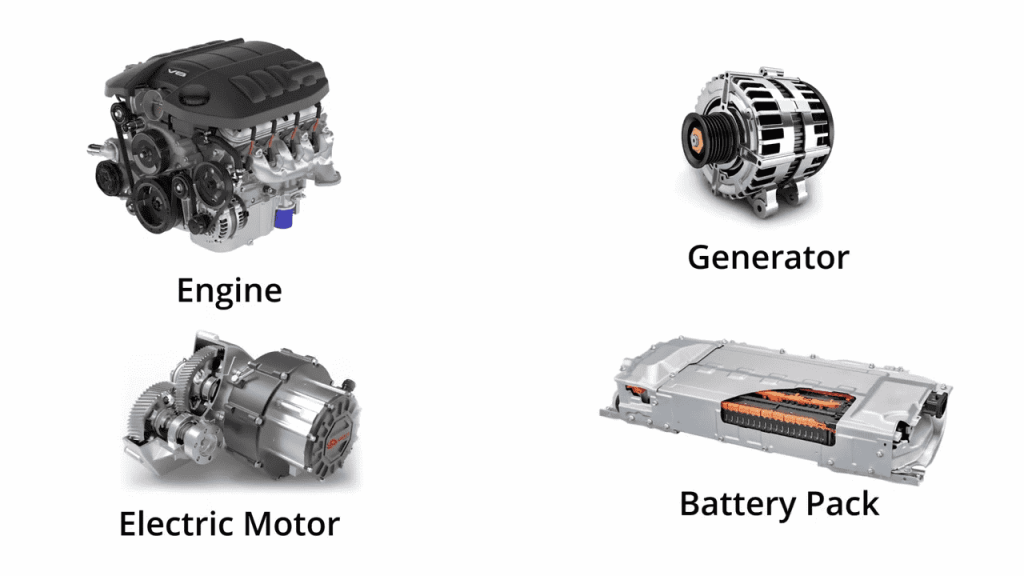
Components of a Hybrid Car
Internal Combustion Engine
Hybrids are famous for their usage of electric motors, but they still need the gasoline engine for lengthy drives and higher velocities. Like the electric motor, the job of this engine is to complement the engine.
Electric Motor
It tackles low-speed operation independently and assists the gasoline engine during a power surge using the stored charge in the battery pack.
Battery Pack
The battery supplied energy to the electric motor, and this pack was used to store the energy. This battery is typically fully rechargeable in full hybrids and plug-in hybrids either through regenerative brake and/or by connecting to an outside power supply.
Power Control Unit
This component controls the power distribution of the car by the gasoline engine, electric motor, and battery pack. This ensures that the car runs to the optimum by choosing the right power source depending on the manner of driving.
How Do Hybrid Cars Work?
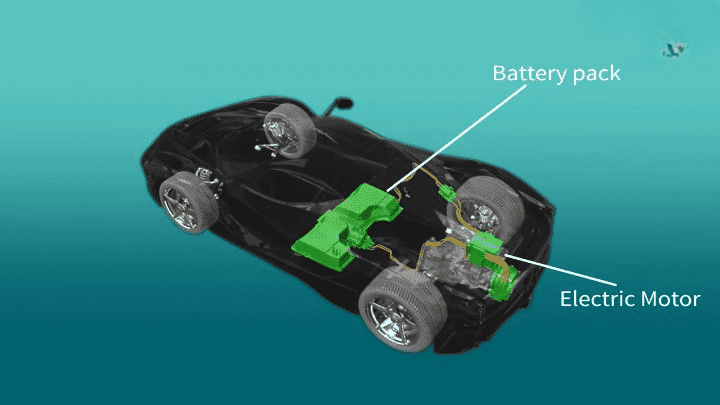
The Hybrid System
Power Split Device
Another feature that may be employed in most hybrid cars is a power split device that assists in controlling the power of the engine and the electric motor. This enables the car to switch very fluidly between running on purely electric power, purely gasoline, or both.
Regenerative Braking
Regenerative breaks are used in hybrid cars and are one of the major components. It retrieves energy that would have otherwise been wasted on the braking system and converts it into electricity to be stored in the battery. It improves fuel economy and wear and tear on the brakes.
Different Driving Modes
Electric-Only Mode
This mode is where the vehicle is operated entirely on electricity, with a tendency to do this at low speeds for short distances. More suitable for city traveling and will assist in saving gas and lessening pollutants.
Hybrid Mode
Hybrid mode is when both the electric motor and gasoline engine are in use at the same time. Based on the car’s system, the different power sources are used at certain time intervals to ensure optimal use.
Engine-Only Mode
Its power output may be sufficient to manage the car at high speed or when the battery is not well charged and can only use the gasoline engine. This mode gives the power required for high speed on the highways while storing the energy in the battery for use later.
Energy Management in Hybrid Cars
Charging the Battery
The use of energy is self-contained in hybrid cars by regenerative braking and, in the case of plug-in hybrids, external charging. This helps to keep the battery charged always so that it can support the engine in cases where this is required.
Energy Flow During Acceleration and Deceleration
The accelerator pedal works as follows: During acceleration, the electric motor boosts the power to light the engine load. During deceleration, energy regained from motion is then stored in the battery for use during acceleration.
How Hybrid Cars Improve Fuel Efficiency
Role of Electric Motor in City Driving
In city stop-and-go conditions, its operation is taken over by an electric motor, resulting in considerable savings in fuel. The gasoline engine is also capable of decoupling completely when not needed.
Efficiency on Highways
As much as hybrids are most suitable for urban areas, they also do well under interstate driving. Electric and gasoline power enables cruising, and the battery is recharged by regenerative braking.
Types of Hybrid Cars

Full Hybrids
Series Hybrids
In series hybrids, the electric motor is the chief means of propulsion, while the petrol engine works by recharging the battery.
Parallel Hybrids
Compared to the series hybrids, the parallel hybrids allow both the electric motor and the gasoline engine to work at the same time to power the vehicle and offer power and efficiency.
Mild Hybrids

Mild hybrids still have a smaller electric motor to help the gasoline engine but can only run on electric power for a shorter period. These are better than normal cars for efficiency and emissions but not as complex as full hybrids.
Plug-in Hybrids
Advantages of Plug-in Hybrids
Plug-in hybrids can be recharged with the help of an external power supply, which makes it possible to top up the onboard electric-only driving ranges. They offer the best of both worlds: electric driving for short distances and gasoline power for long distances.
Advantages of Hybrid Cars
Here are five advantages of hybrid cars in bullet points:
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: Uses gasoline and electric power with the aim of minimizing fuel utilization mainly for urban use.
- Lower Emissions: The emissions of greenhouse gases are lower than those of other traditional gasoline vehicles. Hence, the environment is rated less.
- Cost Savings: Longer lasting and can potentially provide lower fuel consumption and government rebates, which would offset the initial cost of purchasing the hybrid vehicle.
- Smooth and Quiet Driving Experience: It gives a smooth and quiet operation, especially in electric-only mode, which can be described as quieter and all-at-once torquey.
- Regenerative Braking: This technique retrieves energy during braking to charge the battery, thus increasing the brake system’s efficiency.
Final Words
Such cars are more advanced than the conventional ones with a combination of aspects of gasoline and electric-powered cars. It has been established that they have a number of advantages, such as better fuel consumption and emission rates, and this has made them popular with many drivers. In the future, hybrids are expected to become important in the transition to a state that is more friendly to the environment.
FAQs
How long do hybrid car batteries last?
Hybrid car batteries typically last between 8 to 15 years, depending on the model and usage. Most manufacturers offer warranties that cover the battery for at least eight years or 100,000 miles.
Are hybrid cars good for long-distance travel?
Yes, hybrid cars are suitable for long-distance travel. While their electric range may be limited, the gasoline engine ensures you can cover long distances without needing to recharge frequently.
How often do you need to charge a plug-in hybrid?
The frequency of charging depends on your driving habits. If you mainly drive short distances, you may need to charge daily. However, for longer trips, the gasoline engine can take over, reducing the need for frequent charging.
What happens if a hybrid car runs out of battery?
If a hybrid car’s battery is depleted, the gasoline engine will take over, ensuring you can continue driving without interruption. In the case of a plug-in hybrid, you’ll still be able to drive using gasoline power.
Can hybrid cars run on electricity alone?
Yes, many hybrid cars can run on electricity alone, particularly when driving at low speeds. However, the range is limited compared to fully electric vehicles, and the gasoline engine will engage when more power is needed.

