In this case, any driver should know how to jump-start the car. This way, they can protect themselves from being in a helpless situation and assist others in a similar position. Nonetheless, comprehending the specificities, such as how many amps are required, is vital for getting it right and for safety purposes. This guide will endeavor to lay out the relative specifics of jump-starting your car, including the amperage and more.
It is very useful and even sometimes necessary to know how to jump-start a car. This is the right way of doing it, whether you are the one who has a dead battery or you are helping another person. An important part of this process is learning as many amperes are required to start the car. In this article, you will find all the information needed on car batteries, starting with a general overview of what they are and the required amperage when in a particular situation.
What is a Car Battery?
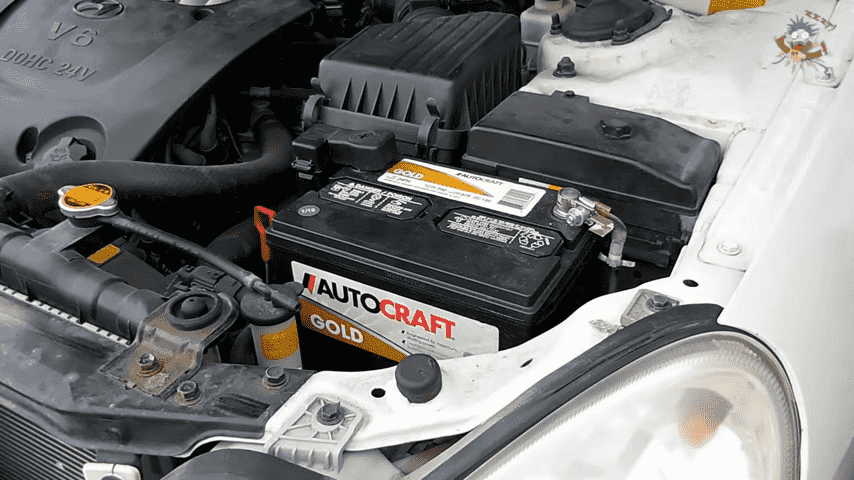
A car battery is the internal combustion engine’s electrical center or the electrical powerhouse. It supplies the needed power to run electrical systems, including the engine, when the engine is not functioning. Common car batteries are lead-acid batteries because they are very trustworthy, and compared to other types of batteries, they are not very expensive.
How Does Jump-Starting Work?
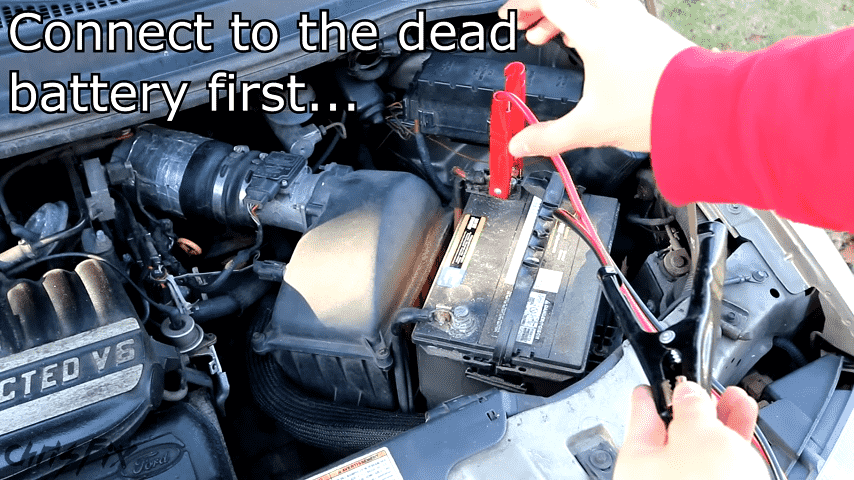
The starting of a car involves the application of boost energy in the shape of electric energy to initiate the action of the car engine. This can be done with another vehicle using a battery and cables where one car will act as the donor car and the other car as the recipient car or using a portable jump starter. Aiming at any of the above methods is to give a temporary jump start to the dead battery so the car can start.
The Role of Amperage in Jump-Starting
Definition of Amps
Another form of electrical current is amperage, commonly referred to as amps, which is the rate at which electric current flows. It is vital to start a car since it establishes the amount of current that is to be provided to the dead battery.
Why Amperage Matters in Jump-Starting
The number of amperes required to jump-start a car also varies with the size of the car and the capacity of the battery. If there is not enough amperage, the car will not start; on the opposite, too much amperage will end up damaging the battery or the electrical system.
Typical Amperage Requirements
Standard Car Batteries
Every standard car battery needs a jump-start of 400 to 600 amps. This range is enough to crank up the majority of small to mid-size compact cars in normal circumstances.
Variations Based on Vehicle Type
Trucks, SUVs, and other larger vehicles may require more current; usually, anything larger than your average car would require somewhere between 700 and 1000 amps. Here, motorcycles and small cars require only 200 to 300 amperes of current, and big cars or trucks require about a hundred more than small cars or motorcycles.
Factors Affecting Amperage Needs
Battery Condition
Also, the amperage taken to jump-start the battery will be minimal if the battery under jump-starting is well-maintained as compared with the old or poorly maintained battery. Frequency also plays a major role in preventing the dead battery crisis; therefore, checks and maintenance should be routinely done.
Vehicle Size and Engine Type
The big engines require more current to crank over; therefore, the amperage is higher. For instance, starting, lighting, and charging demand more amps of Diesel engines compared to gasoline engines because the former has a higher compression ratio.
Temperature and Weather Conditions
Battery life may be greatly affected by cold weather conditions. Because the engine is hard to turn over in cold weather, a higher amperage jump starter might be needed.
Safety Considerations
Importance of Following Safety Protocols
Starting of automobiles involves high electrical currents that can be potentially lethal if one is not very careful. One should always be sure to adhere to traffic rules in order to avoid accidents or damage to the vehicle.
Common Safety Mistakes to Avoid
- Connecting cables incorrectly
- Battery starting with different kinds of batteries
- Overlooking the symptoms of a bad battery
Steps to Jump-Start a Car
Detailed Step-by-Step Guide
- Prepare: Locate the donor vehicle in a manner that the cables will be able to get to both batteries but must not come in contact with the batteries.
- Connect: Couple the red (positive) wire to the positive terminal of the dead battery and then to the donor battery’s terminal. The other end of the black (negative) cable connects to the negative terminal of the donor battery and any other metallic bare area of the dead car.
- Start: Engage the donor vehicle and allow it to run for response time, usually for a few minutes. After that, attempt to restart the dead car.
- Disconnect: After the car battery has been charged, disconnect cables in the reverse manner used to connect them.
Tips for a Successful Jump-Start
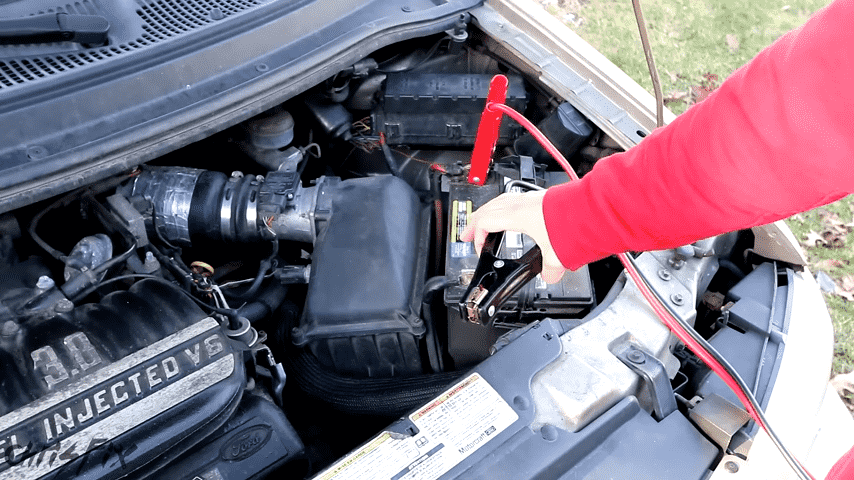
- Check that all the connections are tight.
- Do not come close to the metal clamps when the cables are already connected.
- Ensure that the donor vehicle is always in motion during the process.
Choosing the Right Jump Starter
Types of Jump Starters
Portable jump starters: Small and portable – for use in the case of an emergency.
Battery chargers: These are more applicable to maintaining the battery’s health rather than jumping-starting the car in emergency situations.
Key Features to Look For
- Amperage rating fit for your car
- Built-in safety features
- Durability and reliability
Portable Jump Starters vs. Traditional Jumper Cables
Pros and Cons of Each Method
- Portable Jump Starters are convenient; you don’t need an additional car. Nevertheless, they have to be charged over and over again.
- Traditional Jumper Cables: Reliable for the most part and not complicated, but require an additional vehicle.
Conditions Most Suitable to Each
There is no company alone or in a secluded area; therefore, use a portable jump starter.
Conventional jumper cables are effective when other vehicles are around.
Common Myths About Jump-Starting
Debunking Popular Misconceptions
- Myth: This means you can use any of a kind to start another of a kind.
- Fact: One should make sure that the donor vehicle has a compatible battery.
- Myth: There are no restrictions concerning your state or the car when you jump-start it.
- Fact: Hazard: In wet conditions or if it is rainy, the chances of getting an electric shock might arise.
Conclusion
Starting a car is a skillful practice that can be essential in most instances to help one avoid the inconveniences of seeking assistance. Knowing the amount of current that is needed and following the right course of action, one can very well execute the jump-starting of a car. It is suggested that you do battery maintenance from time to time and ensure you are equipped with the proper equipment.
FAQs
How often should I check my car battery?
It’s a good idea to check your car battery at least twice a year, especially before winter.
And summer.
Can jump-starting damage my car?
If done correctly, jump-starting is safe. Incorrect procedures can damage the battery or electrical system.
How long should I let my car run after a jump-start?
Let your car run for at least 15-30 minutes to allow the alternator to recharge the battery fully.
Is it safe to jump-start a car in the rain?
It’s best to avoid jump-starting in wet conditions due to the risk of electrical shock. necessary, take extra precautions to stay dry.
Can a completely dead battery be jump-started?
If a battery is completely dead, it might not hold a charge even after a jump-start. In such cases, a replacement may be necessary.

