Over the years, there has been a significant shift in automobile technologies, and one that has gained popularity is power steering. When driving on a busy, uneven street or simply going for a highway drive, power steering has become a handy tool. So, why might power steering be a highly valued addition to modern cars? Well, will you please come along with me and look with my eyes?
The Evolution of Power Steering
Old-fashioned vehicles were usually equipped with manual steering systems, which could be significantly demanding in terms of the effort needed to turn the wheel, especially at low speeds. However, the implementation of power steering, seen in the middle of the twentieth century, was another revolution that offered driver’s assistance. In the recent past, technology has improved the state of the art of power steering systems to improve efficiency and durability.

Types of Power Steering Systems
Power steering systems can be of two types, namely, hydraulic response power steering systems and electronic power steering systems. Hydraulic power steering, electric power steering, and electro-hydraulic power steering are the three main species.
Hydraulic Power Steering (HPS)
HPS works through the use of hydraulic pressure sourced from a pump that is run by the vehicle’s engine for enhanced steering. It has been used for many years, and for a good reason – it is simple but efficient. Additionally, the Service AdvanceTrac system in Ford vehicles ensures stability and control, making driving safer and more reliable.
Electric Power Steering (EPS)
EPS, in contrast, utilizes an electric motor for assistance in the steering process and is not as precise as the HPS. This has its advantages over the traditional system, which includes higher energy efficiency and more options to manage and adjust the system.
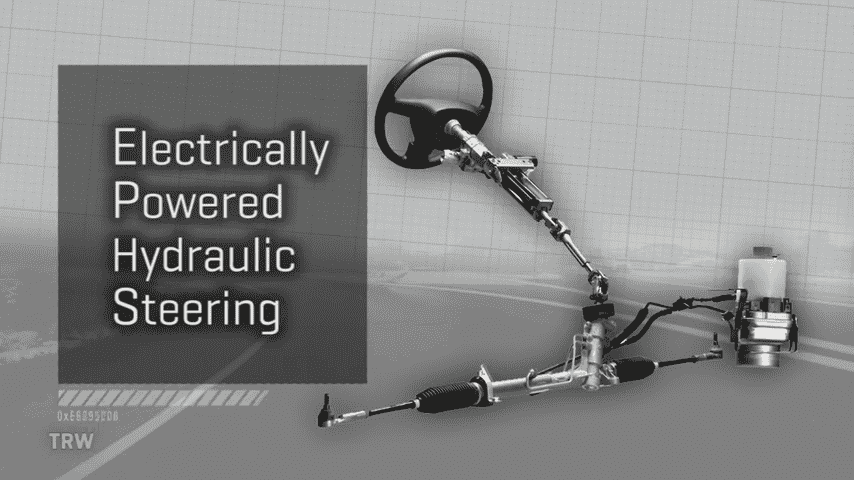
Electro-Hydraulic Power Steering (EHPS)
It employs the features of hydraulic and electric systems, although it uses electricity to turn the hydraulic pump. This model is an attempt to get the best of both worlds, where students study in a conventional classroom at their university and attend meetings in a traditional face-to-face format via a computer link with their fellow students at another faculty.
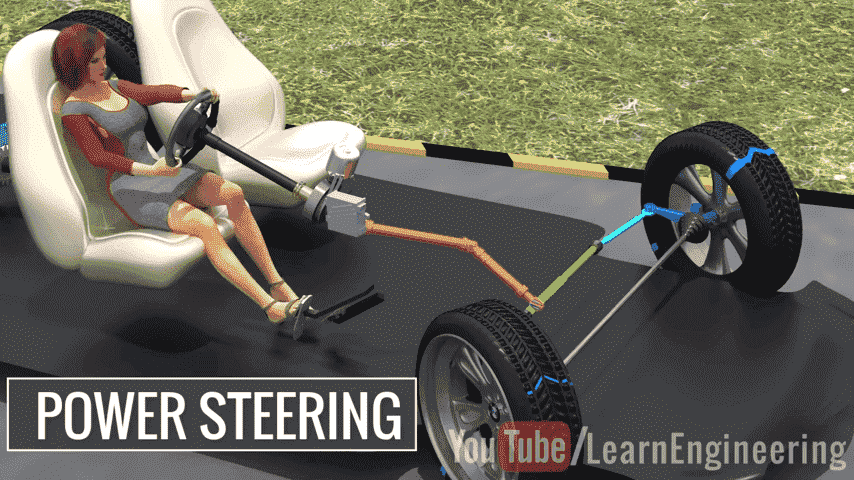
How Power Steering Works?
In simple terms, power steering lowers the amount of effort felt by the driver to manipulate the steering wheel in an effort to make it easier to turn the wheel. There are several parts within a power steering system, such as the steering pump, fluid reservoir, steering gear, hydraulic lines, or the electric motor, depending on which type of system is involved.
This power is provided to steerage by increasing the pressure of the fluid by a steering pump situated near the gear. In an EPS system, a small electric motor works with the steering and does not involve fluid. If you ever hear an engine ticking noise, it could indicate issues with the hydraulic system or other engine components, requiring immediate attention.
Advantages of Power Steering
- Enhanced Maneuverability: It can also maneuver through narrow streets and is easier to maneuver when parking.
- Reduced Driver Fatigue: The steerer and steered axles can be interchanged, and less effort is needed to steer.
- Improved Safety: Ability to maneuver the car in various positions for a shorter time in case of an emergency.
- Better Control: This ensures better and more precise control over the output of steering, thus improving the car’s handling.
Hydraulic Power Steering (HPS)
Mechanism of HPS:
The HPS system works through the engine-driven pump that produces hydraulic pressure within the system and then transmits it through hydraulic lines to the steering gear. This pressure helps the steering gear to turn more easily and helps the wheel to turn with less force.
Pros and Cons of HPS
Pros:
- Maintains the much-needed consistency in the feedback provided by the steering mechanism
- Stable and proven means Reliable and well-understood technology has high stability and predictable characteristics of its functioning, so there is a high level of confidence that it will fulfill its functions at a given level and without additional interference.
Cons:
- Constant operation of the pump makes it less fuel efficient than the conventional oil pump.
- It is also evident that the more components exist, the greater the maintenance necessary to prevail over any variation.
Electric Power Steering (EPS)
Mechanism of EPS:
Miniature epicyclic gear EPS systems employ an electric motor on the steering column or rack to assist. It measures the force of the driver’s steering and accordingly controls the extent of support from the motor.
Pros and Cons of EPS
Pros:
- Increased fuel economy as the motor is not constantly on and running Eaton’s hybrid system.
- Less costly, more flexible to the type of driving or the environment it is being used in
Cons:
- It still could feel less natural compared to hydraulic systems
- In most cases, repair or replacement of the machinery attracts higher costs
Electro-Hydraulic Power Steering (EHPS)
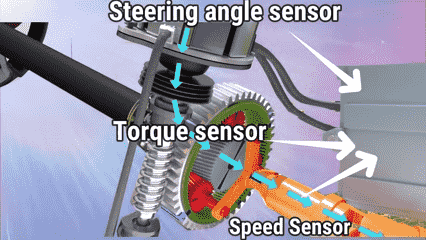
Mechanism of EHPS
EHPS employs an electric motor by incorporating it within the hydraulic system, acting as the hydraulic pump. This setup gives the advantages of hydraulic operation in terms of force supply and, simultaneously, the benefits of electric operation in terms of control and energy consumption.
Pros and Cons of EHPS
Pros:
- Being able to sustain the workers’ productivity and, at the same time, achieve efficiency is a crucial goal that many procedures aim to identify and realize.
- The fact that a great number of vehicles use similar screws makes it possible to quickly adapt it to other types of automobiles.
Cons:
- Overall, a more complex system that a building owner might be willing to pay a higher upkeep?
- It can be more expensive in terms of its initial cost.
Power Steering in Different Vehicle Types
Power Steering in Passenger Cars
EPS is commonly used in most modern passenger cars mainly because it is highly efficient and its size is comparatively small. Some of the critical areas include the improvement of the dynamics control, dynamics experience, and steering.
Some key areas include dynamics control, dynamics experience, and steering.
Power Steering in Commercial Vehicles
The HPS or the Enhanced HPS is more common in light commercial vehicles; they are employed in trucks and vans, which have more ways when it comes to load and frequent stopping.
Power Steering in Heavy-Duty Vehicles
For instance, HPSs used in construction equipment or large trucks will require optimal performance as vehicles are rugged and highly sensitive to environmental conditions.
Maintenance of Power Steering Systems
This article seeks to equip the reader with adequate knowledge and understanding of how to maintain power steering systems so as to enhance their durability and efficiency. Power steering is another crucial aspect that should be checked and serviced regularly, tasks that entail checking the fluid, the hoses, and the belts, as well as checking for any leaks in the system.
Future of Power Steering Technology
The future of power steering looks promising and holds a lot of potential, with emerging trends gravitating towards being upheld within the paradigm of smart and semi-autonomous driving. New technologies that will give attributes like Steer-by-wire that remove the link between the steerage wheel and the wheels are seen offering additional precision as well as safety.
Power Steering and Fuel Efficiency
Power steering can affect fuel economy by using energy to assist in turning the wheels, mainly in hydraulic systems where the pump is an engine accessory. The EPS systems that function when required only to power juices are more fuel efficient and thus decrease the overall consumption of fuel.
Conclusion
Steer assist has, therefore, greatly transformed how people drive and use their automobiles, as it makes automobiles more manageable, safe, and comfortable to steer. Whether it is the seamless running of EPS, the control and efficiency provided by HPS, the synergy of EHPS, or combinations provided with all of them, power steering is an indispensable part of modern cars that improve driving in as many ways as possible.
FAQs
Exploring the factor of how power steering facilitates safety in automobiles.
However, power steering makes a car safer to drive by allowing the driver to steer easier and faster, especially when there is an emergency.
What is the difference between hydraulic and electric power steering?
Hydraulic power steering operates with the help of hydraulic fluid and a pump, whereas an electric power steering operates with an electric motor to assist the power steering and there are advantages such as enhanced fuel efficiency and also better customization.
How frequently should power steering fluid be replaced?
Generally, it is recommended that power steering fluid be renewed between 50,000 and 75,000 miles. However, in order not to establish yourself on an incorrect foundation, it’s advisable to adhere strictly to the manufacturers’ recommendations.
Is it possible for me to drive a car with a power steering that has been taken out?
Although it is possible to drive a car without this feature, it will be much more exhausting, especially at slow speeds, and maybe a real headache and a menace to other drivers.

