Have there been times when you were worried they would store your reliable car battery in such a manner that you could only be left with a $300 paperweight? It may also overly concern the possible risks associated with the battery, for instance, finding itself struggling to dispose of the acids safely or being shocked when handling or storing a battery. You’re not alone. This issue creates a lot of problems for many car owners, which turns them into users who look for comprehensible information. Well then, let me briefly show you how to store your car battery in the most simple way, like a master, so that it is always ready to produce power whenever you need it.
Why Proper Storage Matters?
Measures or procedures regarding car battery storage should also be taken into consideration so as to favor the mere existence of the battery and not take the efficiency of the battery into account alone. Doing so helps prevent the concentration of sulfates, reduces cases of leaks and corrosion, and thus increases the safety and efficiency of the battery. In essence, batteries are harmed by improper storage in an aspect of dying within a given period, during which a particular battery has to be replaced; the batteries are expensive and are of little danger.
What to consider when storing your battery
As much as car batteries are manufactured and supplied in ready-to-use containers, some issues should be considered when storing these batteries for future use. Here’s a comprehensive list of what to consider:
1. Charge Level
Battery preservation entails charging the battery if it is to be stored for some time. It is true that sulfation may take place on a partially charged battery, and this will lead to its having low capacity and life expectancy. During storage, transporting it, or even leaving it in one place for a longer period of time, a battery tender or trickle charger can be of great help in maintaining the charge level of the battery.
2. Cleanliness
Slide the rubber cap from the battery case and use a cloth, brush, or toothbrush to remove the dirt, grease, or corrosion from the battery terminals and the case. Baking soda is effective in tackling acid residue since it has an alkaline nature and can be easily dissolved in water. When charging has been completed, or the battery is fully charged, ensure they are dried before storage.
3. Storage Location
Store it in a position best described as cool, dry, and aerated, as this will help prolong the life of the battery. Both high and low temperatures are not ideal conditions for the batteries. A battery exposed to high temperatures can get damaged very quickly, and the same goes for a battery exposed to low temperatures. High humidity is detrimental, particularly due to corrosion, and although it is not highly wet, it is not optimal either.
4. Temperature Control
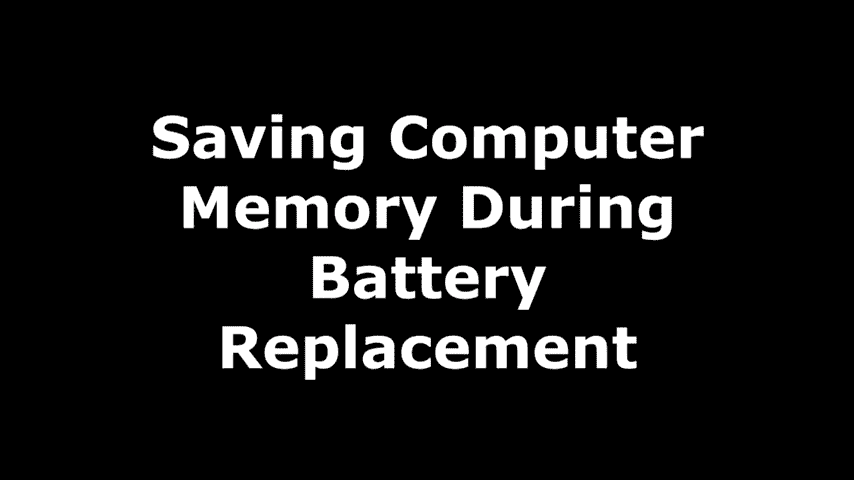
Do not expose the battery to high or low temperatures, as that may damage it. Ideally, it should be kept in cool areas with a room temperature of between 50°F to 70°F (10°C to 21°C). High temperatures increase the Self-discharge rate, and low temperatures can cause the formation of ice and eventually crack the battery if not charged.
5. Ventilation
Make the storage area well-ventilated, as batteries, especially lead-acid ones, emit gases when charged or stored. Fresh air diminishes the tendency for fires and explosions, which is crucial in protecting safety.
6. Insulation from Concrete
Although modern batteries are not as responsive to concrete as previously, it is advisable to stand them on a wooden pallet or a plastic tray. It helps prevent water infiltration into the battery and allows adequate air circulation around the battery.
7. Safety Precautions
To avoid spilling the battery or even getting one’s fingers accidentally trapped, one should be very careful while handling the battery. The hot battery can be dangerous as it might explode or release poisonous fumes; therefore, you should wear gloves and eye protection when carrying out any of the following on the battery: inspecting, cleaning, or moving. To avoid any mishap, ensure that the battery is not within the reach of children or other pets.
8. Terminal Protection
It is recommended that a thin coat of petroleum jelly be applied on the terminals or that anti-corrosion pads be used to avoid the formation of rust while in storage. This will guarantee a positive electrical connection as soon as the battery is placed back in position.
9. Regular Monitoring
The battery should be checked; it is recommended that it be checked on a monthly basis. Finally, a multimeter should be used to check the voltage since it should be healthy and average around 12. 6 – 12. 8 volts for lead-acid batteries. Re-charge if the battery voltage falls below the standard voltage levels we take when in the middle of re-charging.
10. Preparing for Reinstallation
Before replacing the battery, assess it to verify it has undergone damage such as cracking or leakage. Tidy up the terminals and determine how much charge is left. Before using the product for the first time, charge the battery entirely in case of low power, as this will enable the greatest capacity.
Storing Different Battery Types
- Lead-Acid Batteries: Keep fully charged and store in a cool, dry place. Use a battery tender if possible.
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: Store at around 50% charge in a cool, dry place. Avoid extreme temperatures.
- AGM Batteries: Store similarly to lead-acid batteries, but note that they handle cold temperatures better.
Special Considerations for Seasonal Storage
- Winter Storage: Charge the battery whenever the opportunity arises and, if possible, keep the battery indoors as it is vulnerable to freezing conditions.
- Summer Storage: It is also advised not to expose the item to direct sunlight or heat for an extended period. Some handling precautions include: If it is kept in a hot area, the container should be shielded by shading or cooled.
Therefore, in light of these points above, you can adequately store your car battery and thus extend its lifetime while still on standby to be used in cases of need. The longevity of the battery can be preserved, and its efficiency and safety can be ensured if proper storage features are followed.
What’s the longest battery life?
The range of days a car battery will last can vary depending on the type of battery, the usage of the battery, and the level of self-charge maintenance being implemented. Here’s a breakdown of the longest potential lifespans for different kinds of car batteries:
Lead-acid batteries
These are the most common types of car batteries, and they normally last between 3 to 5 years under ideal usage circumstances. Some can last up to 6 years since it all depends on how well they are maintained and used.
Enhanced Flooded Batteries (EFB)
Such ones can slightly last longer than portable lead-acid batteries in offering service for about 4-6 years.
Absorbent Glass Mat (AGM) Batteries
The other category is known as deep cycle batteries, also called AGM batteries, due to their ability to meet tasks with extended utilization time, and they last between 5 to 7 years. If provided with proper care, they might even live for up to 8 years.
Lithium-Ion Batteries
EVs and hybrids with lithium-ion batteries also have longer cycle lifetimes than lead-acid batteries. They can normally serve for 8 to 10 years or even longer. Some high-quality lithium-ion batteries on EVs today have been said to last for up to 15 years; despite this, they require maintenance and should not be overused.
Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Batteries
Effective mostly for hybrid vehicles, NiMH batteries have a normal life expectancy of 6-10 years. High-quality materials are used in construction, which makes them resistant and capable of withstanding too much cycling, hence making them durable.
Factors Affecting Battery Life
Usage Patterns: However, taking many short trips is worse as the alternator charges the battery intermittently, thus giving it little time to charge fully. It is better to use energy and travel at a moderate pace for a long time. So, what’s the best way to charge an electric vehicle properly, and how long?
Climate: This is because high and/or low temperatures affect the lifespan of batteries to a greater extent—moderate temperatures liveleaveteries for longer than conditions that are extreme, either colder or hot.
Maintenance: To ensure long and efficient service by the battery, the battery should be checked often and, if necessary, cleaned and charged to the optimum level.
Storage Conditions: Some ways and measures to avoid battery degradation include: Battery storage is another key area that can be prevented when the battery is not in use. Most battery degradations can be prevented in some ways, including proper storage. This involves storing the battery in a cool and dry area with a battery tender to ensure it provides juice for customary usage.
Maximizing Battery Life
To get the most out of your car battery, consider the following tips:
Regular Maintenance: It is recommended to inspect the battery for any signs of corrosion or leakages, or if the car being tested has battery fluid, check the levels as well.
Proper Charging: One should not allow the battery to run down to a zero percent level of charge. This is especially true if the vehicle is occasionally used and the battery should be charged by a battery tender or charger.
Climate Control: In this case, since it is summer, the heat is quite intense, and this means that one has to park the vehicle in a garage in order to avoid direct exposure to such heat.
Driving Habits: To limit the times the battery is in a weak state due to engine starting, it is advisable to make several short trips in one trip.
Tools and Materials Needed for Storage

Essential Tools
- A wrench or socket is adjusted to loosen the nut and thus disconnect the battery.
- For washing, they use a mixture of baking soda and water as a scrub.
- Multimeter for checking voltage.
Recommended Storage Materials
- I am talking about the battery tender or trickle charger type.
- Container: battery storage box or a simple plastic container.
- Anti-corrosion pads for terminals.
Conclusion
We must first emphasize that it is vital to store your car battery correctly in order to get as much life out of it as possible and also to make sure it is as reliable as possible in the event that it is needed suddenly. Taking the requisite precautions in the manner in which they are cleaned, charged, and stored can also help to avoid any risk of damage to the merchandise and the safety of people handling them. Here are general tips that are applicable to any type of bike battery – lead-acid, lithium-ion, or AGM – meaning that when you store your battery like this, it will be ready to use in the future.
FAQs
How long can I store a car battery?
A properly stored car battery can last several years, but it’s best to check it every few months to ensure it’s maintaining its charge.
Can I store a car battery in my house?
Yes, but ensure it’s in a well-ventilated area, away from heat sources and children.
How do I know if my battery is still good?
Check the voltage with a multimeter. A fully charged battery should read around 12.6 to 12.8 volts.
Is it okay to store a battery on concrete?
Modern batteries can be stored on concrete without any issues, but for added protection, a wooden pallet or plastic tray is always a good idea.
What should I do if my battery leaks during storage?
If your battery leaks, neutralize the acid with baking soda and water, clean the area thoroughly, and safely dispose of the battery according to local regulations.

