Caring for your car’s emission system is essential. Do I need to remind you of the times we have had to take our cars for emission tests? In this post, I’m going to explain the five most common emissions system problems and, more to the point, how to sort them out today.
What is an Emissions System?
To give you a head start, here is a brief look at an emissions system: Your car’s emissions system can be described as an assembly of components that are integrated to minimize the production of toxins within the atmosphere. Some essential are oxygen sensors, catalytic converters, EGR valves, gas caps, and mass airflow sensors.
Top 5 Emissions System Problems
1. Faulty Oxygen Sensor
Influences of a faulty Oxygen sensor
The oxygen sensor determines the quantity of unburned oxygen in your automobile’s exhaust and relays this information to the engine’s computer. If the system is bad, there can be a problem with the fuel economy, rough-running engine or even an emission test.
How to Diagnose
A diagnostic scan tool can check the codes from the car’s computer, and frequently, it will point to a problem with the oxygen sensor.
2. Malfunctioning Catalytic Converter
Signs of a Bad Catalytic Converter
It assists in the reduction of dangerous emissions since it acts as a catalyst to transform toxic emissions into less dangerous substances. These signs incorporate reduced efficiency of the engine, the presence of a sulfur scent, and a check engine light.
How to Diagnose
M focusbad 2 contains detailed methods to detect if the catalytic converter is failing through a visual inspection and exhaust back pressure test.
3. Possible Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Valve problems

Signs of EGR valve issues
The EGR valve is a mechanism that pumps back some of your exhaust gases into the engine to minimize Nitrogen oxide exhaust emissions. If it is not working as it should, then the car may waller, especially when it is idling or accelerating slowly or even consuming more fuel compared to normal.
How to Diagnose
The EGR valve may get stuck or clogged in some cases, and this is how you may diagnose it; with a simple visual inspection or vacuum gauge.
4. Leaky Gas Cap
Symptoms of a Leaky Gas Cap
I’ll be honest; I never thought having a ripped-off or wrongly tightened cap would lead to my check engine light blinking. Other signs include fuel odor and stinging pain that is accompanied by a decrease in the car’s fuel economy.
How to Diagnose
If the gas cap is damaged or cracked, a simple check can tell you if it is causing the problem.
5. Faulty Mass Airflow Sensor
Signs of a Bad Mass Airflow Sensor
The mass airflow sensor is used to determine the air coming into the engine, where the computer regulates the fuel injection. The signs of a bad sensor include low acceleration, rough running, and illuminated check engine lights.
How to Diagnose
The mass airflow sensor can also be diagnosed with a diagnostic scan tool to read the error codes pertaining to that component.
How to Fix Emissions System Problems
Fixing a Faulty Oxygen Sensor
Tools Needed
- Wrench or socket set
- Replacement oxygen sensor
- Anti-seize compound
Step-by-Step Guide
- Find which oxygen sensor is bad.
- Disconnect the electrical connector.
- The old sensor must be unscrewed using the wrench.
- Cob the threads of the new sensor with an anti-seize compound.
- A new sensor has to be installed, and the electrical connector has to be plugged in again.
Fixing a Malfunctioning Catalytic Converter
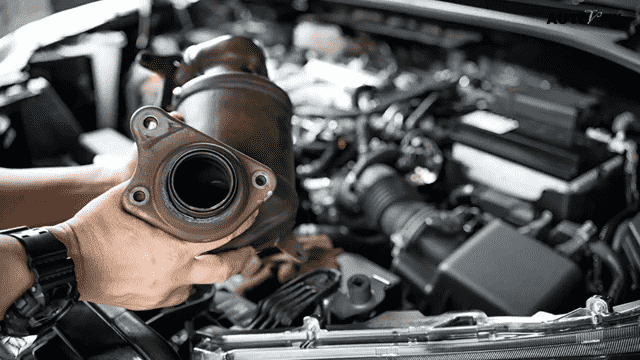
Tools Needed
- Wrench or socket set
- Replacement catalytic converter
- Jack and Jack stands
Step-by-Step Guide
- Lift the car and support it with jack stands.
- Find the catalytic converter and then use a wrench or socket set to undo the bolts that hold it in place.
- Take out the preexisting catalytic converter.
- Fit the new catalytic converter in place and fasten it with bolts.
- Lower the vehicle and then ignite the engine to identify leakages.
Fixing EGR Valve Issues
Tools Needed
- Wrench or socket set
- Replacement EGR valve
- Cleaning solvent
Step-by-Step Guide
- Locate the EGR valve.
- Take out the bolts and disconnect the vacuum line coming from the fuel bowl.
- Containing solvent; wash the valve and the vicinity of it.
- Now that the bent pipe and new EGR valve are in place, reconnect the vacuum line.
Fixing a Leaky Gas Cap
Tools Needed
- Replacement gas cap
Step-by-Step Guide
- Remove the old gas cap.
- Inspect for cracks or damage.
- Install the new gas cap, ensuring it’s tightly secured.
Fixing a Faulty Mass Airflow Sensor
Tools Needed
- Screwdriver
- Replacement mass airflow sensor
Step-by-Step Guide
- Locate the mass airflow sensor near the air filter.
- Disconnect the electrical connector.
- Remove the screws holding the sensor in place.
- Install the new sensor and reconnect the electrical connector.
Conclusion
Your car’s emissions system is vital to keeping your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently. By understanding common problems and knowing how to fix them, you can save time and money and reduce your environmental footprint. Regular maintenance and timely repairs are key to avoiding larger issues.
FAQs
What are the common signs of emissions system problems?
Common signs include a check engine light, poor fuel economy, rough idling, and unusual exhaust smells.
How often should I check my emissions system?
It’s a good idea to include emissions system checks in your regular vehicle maintenance schedule, typically every six months or as your vehicle’s manufacturer recommends.
Can I fix emissions system problems myself?
Yes, many emissions system issues can be fixed at home with basic tools and some mechanical know-how. However, complex problems require professional assistance.
What happens if I ignore emissions system issues?
Ignoring emissions system issues can lead to more serious engine problems, decreased fuel efficiency, failed emissions tests, and increased pollution.
How much does it typically cost to repair emissions system problems?
The cost can vary widely depending on the problem and vehicle. Simple fixes like replacing a gas cap can be affordable, while more complex repairs like a catalytic converter can be more expensive.