Care to know what makes the battery of your car fully charged and all the electrical devices in it to be fully functional? It’s still the alternator, and the diode is critical to this system. Drawing knowledge about diodes and how they work with alternators can shed some light on one of the mysteries of the internal world of any vehicle.
What is a Diode?
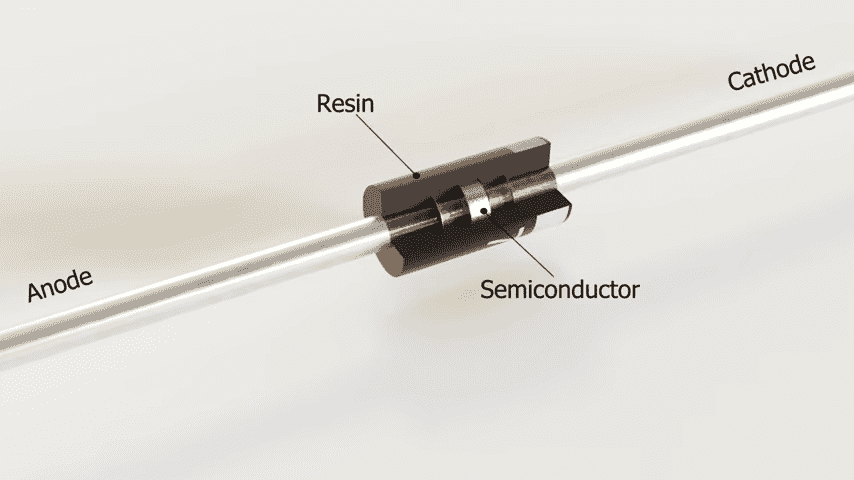
A diode is a semiconductor device that allows electricity to flow in only one direction, offering a one-way passage to the electric current. It is like a filter that allows electrical energy to flow in one direction only and not in the other.
Diodes have been around since the early twentieth century and have been widely used in various circuits of electronics. Some of the most distinguishing attributes that define the diodes include forward-biased current, low forward voltage drop, and high reverse energy.
Types of Diodes
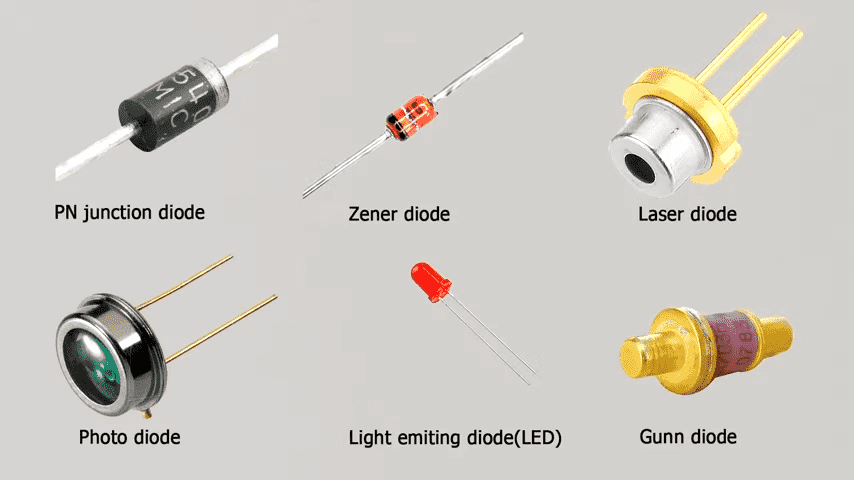
- Standard Diodes: It is widely utilized in rectification processes to disperse the heat evenly.
- Zener Diodes: These are used to control current in the reverse direction as the voltage reaches a certain value, which makes them useful in voltage regulation.
- Light-emitting diodes (LEDs): Incandescence when electric current passes through them. These LEDs are used widely in lighting and indicators.
- Schottky Diodes are widely known for their low forward voltage drop, particularly when switching at a high frequency.
How Do Diodes Work?
Diodes are semiconductor devices in which an electrical current can only flow in one certain direction: in the forward direction when a certain voltage greater than a diode voltage drop is reached, and in the reverse direction when the current cannot flow and is suppressed.
Due to this property, they are very useful in a converter that will convert from the alternating current (AC) to the direct current (DC).
Applications of Diodes
Diodes are also used in the regulation of power supplies, the demodulation of signals, and the protection of circuits against overvoltage. In the automotive environment, they are very important when it comes to maintaining the reliable performance of the alternators and the electrical system in a car or another type of vehicle.
What Is An Alternator?
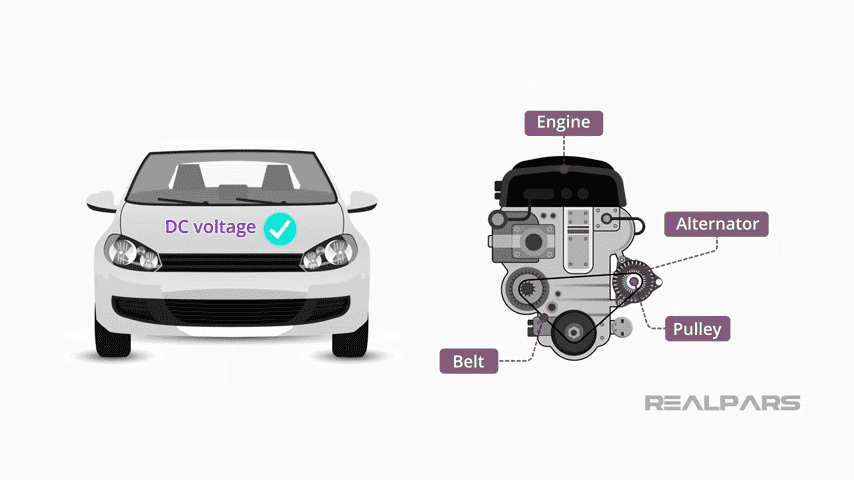
An alternator is a specialized type of generator that produces alternating current from mechanical energy a vehicle uses. In cars, the alternator recharges the battery and the electrical system in the automobile through charging with the help of the generator system when the engine is being used.
Components of an Alternator
- Rotor and Stator: Encases a rotor, which rotates in its stator, to create an alternating current.
- Voltage Regulator: It helps regulate the output voltage within a particular limit required in other circuits.
- Rectifier Assembly: This assembly develops AC electricity from the alternator, which is then converted to DC to charge the battery and power the vehicle’s electrical systems.
The Role of Diodes in an Alternator
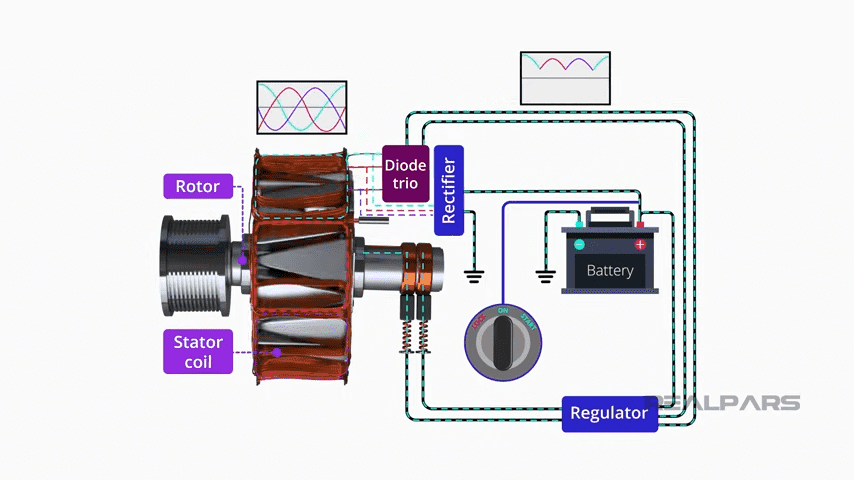
For starters, an alternator is a device used to generate electrical power and can be found in vehicles and other electronics. Diodes are electronic components with two terminals that allow current to flow in one direction only. Now, when it comes to the function of diodes in an alternator, they are used for the following purposes.
Diodes are mainly used to rectify the output voltage of the alternator. Alters. Correct one data review. Chuck converts the AC generated by the rotor and stator into DC to provide a sure and consistent voltage supply to the electrical appliances in the vehicle.
The Rectifier Assembly in Alternators
Today, we want to draw your attention to the rectifier assembly, an important part of the alternator. It usually entails placing multiple diodes in a proper connection for proper AC to DC conversion. Unless the alternator is fitted with these diodes, the system cannot generate the necessary DC power.
Types of Rectifiers Used in Alternators
- Half-Wave Rectifiers: This method is less efficient when using a single diode to rectify half of the AC wave, resulting in only half of the AC signal being rectified to DC.
- Full-Wave Rectifiers: Multiple diodes rectify both halves of the AC wave more effectively than a single center-tapped full-wave rectifier.
- Bridge Rectifiers: This is a particular type of FULL-WAVE RECTIFIER that utilizes four diodes in a bridge format and gives maximum conversion efficiency.
Why Diodes Are Crucial in Alternators?
There are several reasons as to why diodes are important in alternators and they include the following: The chief purpose of using diodes in an alternator is as a rectifier of AC to DC to charge the battery.
First and foremost, diodes are
Diodes facilitate the proper and accurate conversion from AC to DC. They also prevent the backfeed flow of current, which is dangerous to the electrical installation. Their function in excluding backflow current prolongs the lifespan and efficiency of auto electrical systems.
Common Issues with Diodes in Alternators
- Overheating: In particular, overloaded diodes, that is, diodes that are passed an excessive current, may overheat, leading to failure.
- Wear and Tear: However, it is key to know that diodes, like any other component, are only rated to last for a certain number of years or hours.
- There are various symptoms of diode failure: Headlights and warning lights that are dull or weak, and deceased battery warning.
Final Words
Diodes are another critical component in alternators, all associated with the aspect that they perform. They guarantee proper rectification of the AC to DC, help to prevent back-flowing currents and play a part in the over-zenith of a given automobile electrical arrangement. It also contributes to the efficient performance of a car, and it’s crucial to understand how the alternator works and its role in the vehicle’s functioning.
FAQs
What happens if a diode in an alternator fails?
A bad diode in an alternator can be very dangerous because it can result in low access power production for the alternator, draining the battery and causing electrical problems with the car.
Can I use the diodes in the circuit instead of using the alternator?
Some of them are replaceable, but such actions would preferably be done by technicians and may need specific tools. Due to this, it is sometimes advantageous to replace the whole rectifier assembly or the alternator.
How do you test the diode in an alternator?
Measuring a diode involves using a multimeter to check the ohms or kilohms to determine the continuity of the diode in forward and reverse bias. For a diode to work efficiently, it should allow current to flow through in one direction only but not in the other direction.
Can an alternator have other kinds of diodes aside from silicon ones?
Modern, commonly used diodes are among the most efficient and practical components for alternators for rectification. However, new technologies are still not incorporated into organizations because they are complicated and expensive.
How long do diodes in alternators typically last?
Diodes in alternators can last up to 5 years without requiring any interventions if the operations are going on as usual. These factors include excess heat, overcurrent, or when they are not well maintained for a long time.

